
Separations on reversed-phase media are usually done in mixtures of aqueous and organic solvents, which are often denaturing conditions. Serum albumin is primarily composed of helices, thus it would require hydrophilic amino acids to be soluble in the blood. LEUCINE is most hydrophobic among these amino acids.

The neutral form of an amino acid is shown: in solution at pH 7 the amino and carboxylic. Different amino acids are distinguished by their different side chains, R. Think of serum albumin, this a globular protein that is in the blood plasma. most hydrophobic (1pt) Arginine Aspartic Acid Leucine Serine Tyrosine. The backbone is the same for all amino acids and consists of the amino group (NH2), the alpha carbon and the carboxylic acid group (COOH). For this reason, one generally finds these amino acids buried within the hydrophobic core of the protein, or within the lipid portion ofthe membrane. the part of the side-chain nearest to theprotein main-chain): Hydrophobic amino acids are those with side-chains that do not like to reside in anaqueous (i.e. alpha helices may be composed of hydrophilic amino acids. Very hydrophobic amino acids: Less hydrophobic amino acids, or indifferent amino acids: Amino acids that are part hydrophobic (i.e. Samples are loaded onto the matrix in a high-salt buffer and elution is by a descending salt gradient. Hydrophobic because they are transmembrane proteins. Separations on HIC matrices are usually done in aqueous salt solutions, which generally are nondenaturing conditions. Hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC) and reversed-phase chromatography (RPC) are two separation methods based on the interactions between the hydrophobic moieties of a sample and an insoluble, immobilized hydrophobic group. The energetics of hydrophobic bond formation drives amino acids with hydrophobic sidechains into the interior of proteins, in most cases this is a very. In addition, many hydrophobic amino acids are exposed on the surface and it is these that give a native protein its degree of hydrophobicity. Hydrophobic interactions stabilize the tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins. Certain amino acids are hydrophobic in order of decreasing hydrophobicity, they are tryptophan, norleucine, phenylalanine, tyrosine, leucine, valine, methionine, and alanine. Five of the six most hydrophobic amino acids have T as the middle base. The degree of hydrophobicity of a protein is dependent on its amino acid sequence. Thus, all amino acids formed from the precursor pyruvate share the same first.
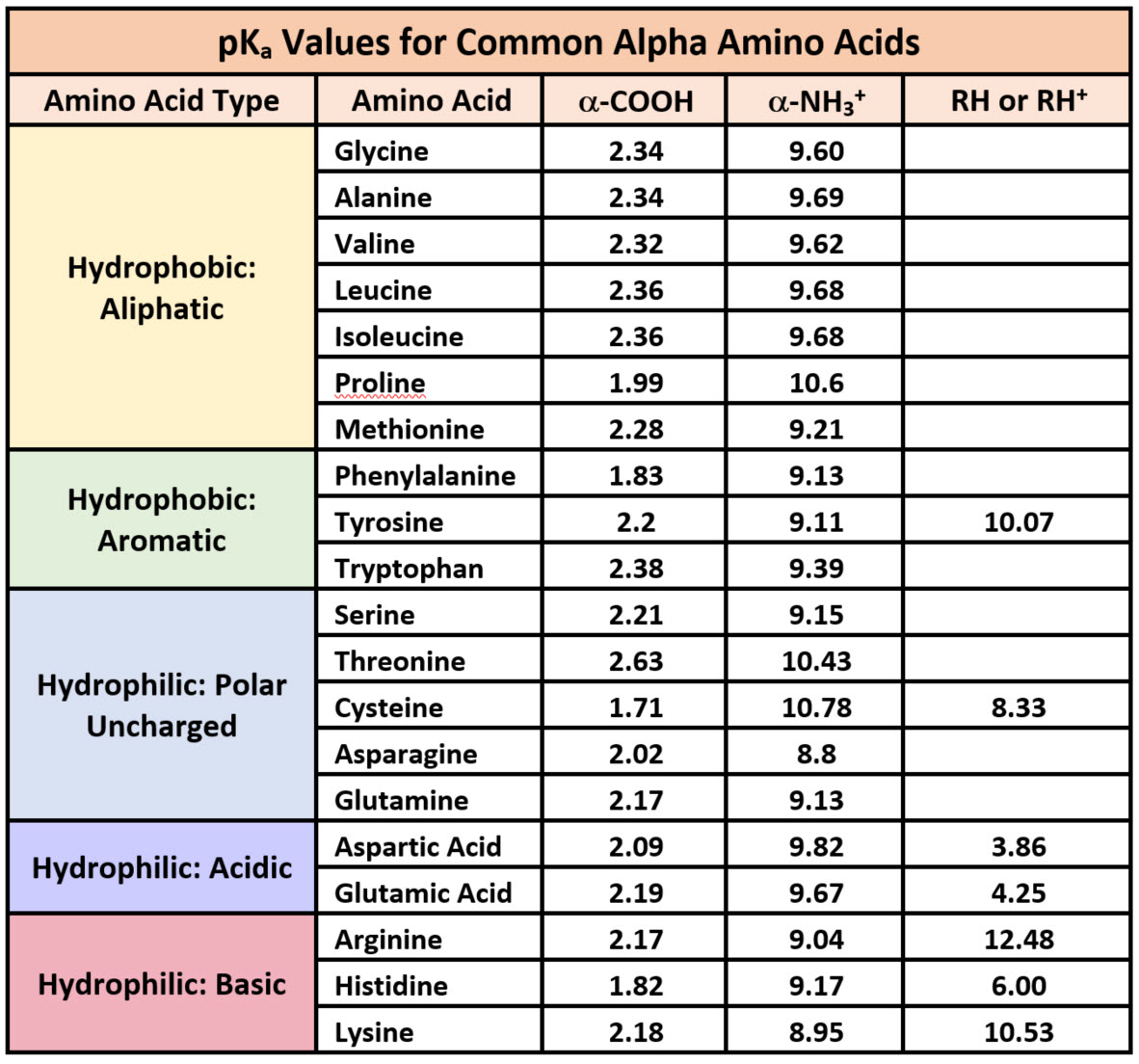
Most aliphatic amino acids are found within protein molecules. Hydrophobicity increases as the number of carbon atoms on the hydrocarbon chain increases. Aliphatic amino acids are non-polar and hydrophobic. It is the structure of the water that creates hydrophobic interactions. An aliphatic amino acid is an amino acid containing an aliphatic side chain functional group. Hydrophobic interactions are forced on nonpolar compounds by the polar environment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
